Assessment of dengue mosquito breeding sources at Pulicat, Tamil Nadu, India
Author(s): Luz Cuello, Samuel Tennyson and Rajasingh Raveen
Abstract: Dengue Fever (DF) is a viral disease transmitted by female adult mosquitoes, Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Until a vaccine becomes available for public health use, primary prevention of transmission is crucial to decrease the burden of dengue, and the control of Aedes species is the only available stratagem. A cross sectional study was conducted at Pulicat village, Tamil Nadu, India. A survey was conducted in a total of sixty nine houses in order to assess mosquito breeding sources for the presence of dengue vector species. Presence of mosquito breeding was confirmed in 56% of the surveyed houses. Both the vector species for dengue transmission were present, with Aedes aegypti as the majority species. This study focused on the prevalence of these vectors in the villages of Pulicat and Vairavan Kuppam as an indicator for the risk of a DF outbreak. However, further studies should consider analyzing other variables that can affect breeding (salinity, disturbance, population density of juveniles), as well as the geographical distribution of houses where breeding is present.
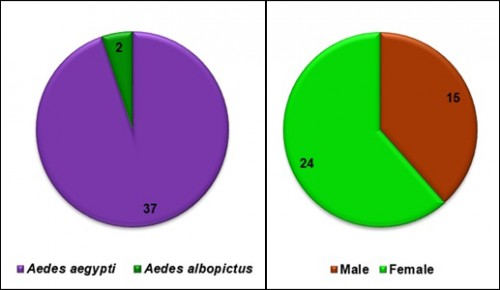 Fig.:
Fig.: Species and sex composition of sampled adult mosquitoes in the study area
How to cite this article:
Luz Cuello, Samuel Tennyson, Rajasingh Raveen. Assessment of dengue mosquito breeding sources at Pulicat, Tamil Nadu, India. Int J Mosq Res 2018;5(3):42-50.



