Molecular characterization of vitellogenesis in anautogenous Culex pipiens pipiens L. mosquitoes
Author(s): Mona G Shaalan, Doaa E Soliman, Mohamed A Abdou, Emad I Khater, Ahmed Othman, Yasser Abd El-Latif and Magdi G Shehata
Abstract: Mosquito vectors-borne infectious diseases are enormous burden on human health and development worldwide. Disease-transmitting mosquito vector species use a reproductive strategy termed anautogeny that requires a blood meal to initiate egg maturation or oogenesis. Understanding the molecular basis of the regulation of egg development following a blood meal is essential to recognize the developmental biology and life cycle of mosquitoes and pinpoint important targets for control interventions. Vitellogenin (Vtg) is the major yolk protein synthesized during oogenesis and widely characterized in many mosquito species, mainly Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes. In this study, we report the differential stage and temporal expression of vtg genes in anautogenous Cx pipiens complex mosquitoes collected from Egypt following the ingestion of a blood meal using quantative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis. qRT-PCR analysis of the transcriptional pattern was performed in adult females at different intervals post-blood meal (pbm) and in developmental immatures. The cDNA of vtg was detected in Cx. pipiens females 24 hours pbm. Sequence analysis of detected vtg disclosed high similarity to homologous sequences in other mosquito species, particularly Cx. quinquefasciatus. Vtg was highly expressed in adult females at 24 h complex, however, in immature stages, only resdiual expression level of vtg was observed. In addition, we tested the presence of Vtg protein at time intervals in ovarian tissues of both sugar fed and blood fed females. Protein analysis revealed that two polypeptides of Vtg protein were detected in blood-fed females but not in sugar-fed females.
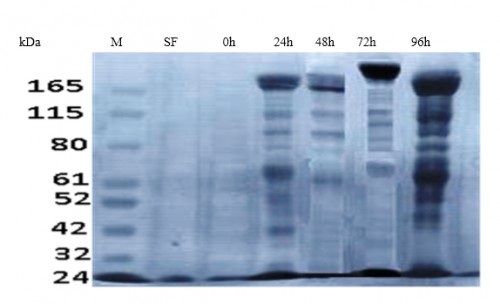 Fig.:
Fig.: SDS-PAGE of total Coomassie Brilliant Blue stained ovarian protein extract (20 mg/ ml). SF: sugar-fed females, 0: immediately PBM, 24 h PBM, 48 h PBM, 72 h PBM, 96 h PBM, M: protein ladder (KDa)
How to cite this article:
Mona G Shaalan, Doaa E Soliman, Mohamed A Abdou, Emad I Khater, Ahmed Othman, Yasser Abd El-Latif, Magdi G Shehata. Molecular characterization of vitellogenesis in anautogenous Culex pipiens pipiens L. mosquitoes. Int J Mosq Res 2017;4(2):05-11.



