Vol. 6, Issue 4, Part A (2019)
Sustainable control of mosquito by larval predating Micronecta polhemus Niser for the prevention of mosquito breeding in water retaining structures
Author(s): Nasiman Bin Sapari, Teh Sabariah Binti ABD Manan and Saba Yavari
Abstract: Urban infrastructures with many receptacles at various sizes for water drainage and supply systems often become potential for water stagnation. This stagnant water can be infested with mosquitoes including the mosquito from Aedes genus that is known as the vector of dengue viruses. Many cases of dengue fever in tropical environment has been reported from time to time. The current method of mosquito control by fogging using chemicals is apparently not effective. This paper suggests an alternative method by bio-control using Micronecta sp. as a predator to mosquito larvae. The physical characteristics, its growth and predatory pattern of Micronecta sp. were investigated in this study. Field observation and experiments were conducted using earth jars to simulate the habitat. The jars were filled with rain water and left as stagnant water in open areas for a period of 3 months. The results indicate that mosquito could not bread in the stagnant water if the environment is established with Micronecta sp. This finding suggests that stagnant water in urban areas of tropical environment may be used for mosquito control by allowing exposure to sun radiation to establish a balance ecosystem.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics
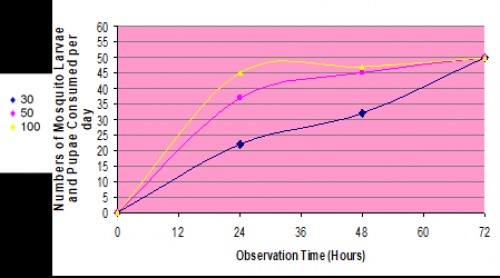
Fig.: Total numbers of mosquito larvae consumed by Micronectidae populations over 72-h period
Pages: 31-37 | 1329 Views 197 Downloads
How to cite this article:
Nasiman Bin Sapari, Teh Sabariah Binti ABD Manan, Saba Yavari. Sustainable control of mosquito by larval predating Micronecta polhemus Niser for the prevention of mosquito breeding in water retaining structures. Int J Mosq Res 2019;6(4):31-37.







