Decline of malaria in Gadchiroli district of Maharashtra state, India
Author(s): RK Singh, Gaurav Kumar, Rajesh Karlekar and A Nayak
Abstract: Globally, malaria is one of the most prevalent infectious diseases, with more than 216 million people at the risk of infection. India is the largest contributor of the disease among the Southeast Asian countries. This study was undertaken to assess the present situation of malaria and its severity, the prevalence of its vectors in Gadchiroli district of Maharashtra. The epidemiological as well as entomological investigations were carried out in 46 villages of three high malaria-endemic PHCs under the Gadchiroli district. Most of the villages are situated in deep forest and forest fringes remote areas of the district. Adult mosquitoes were collected from indoor and outdoor resting, and identified to species level as per the standard keys. A total of 841 blood slides were collected from the local population and examined; of which 227 slides were found positive for malaria parasites (87 for Plasmodium falciparum, 36 for Plasmodium vivax and 104 mixed infection. The mosquito identification revealed 12 mosquito species belonging to the genus Anopheles. In total, 2579 Anopheles mosquitoes were recorded; the average man hour density (MHD) lowest (9.02) for human dwellings and highest (46.98) for cattle sheds. The epidemiological data showed that the malaria transmission in the district occurs throughout the year. Month-wise analysis of malaria reported cases revealed rise in the number of cases from July onwards till attaining peaks in the months of November to January. After the month of February, there was a decline in number of malaria cases with very few cases reported during the months of May to June. Annual trend of malaria showed that the cases declined from 34206 in 2014 to 5484 cases in the year 2017. Therefore, there is a need to strengthen the surveillance in these highly malaria endemic PHCs for containment of malaria.
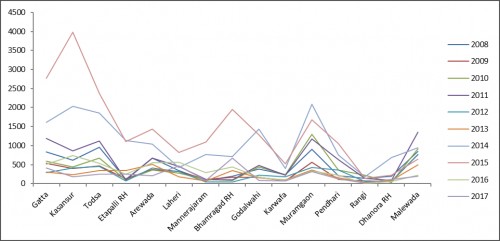 Fig.:
Fig.: Malaria cases in different PHCs of Gadchiroli district, Maharashtra (2008–17).
How to cite this article:
RK Singh, Gaurav Kumar, Rajesh Karlekar, A Nayak. Decline of malaria in Gadchiroli district of Maharashtra state, India. Int J Mosq Res 2019;6(5):20-27.



