Larvicidal efficacy of three sustained insecticides against Culex pipiens larvae
Author(s): Habeeb M Al-Solami
Abstract: Three sustained tablet formulas of the bacterial insecticides Spinosad and VectoBac as well as the insect growth regulator Dudim were evaluated for larvicidal activity against larval stages and pupae until adult emergence of Culex pipiens. Effective control with 90-100% inhibition of adult emergence (% IE) was used as a criterion to evaluate the effectiveness of the test formulations. A high level of residual efficacy with 90-100% IE was achieved for 8 and 11 weeks post-treatment by using tablet formulations of Spinosad and Dudim, respectively. On the other hand, larval treatments with VectoBac tablet formulations showed ineffective control with 63% IE for the 1st week post-treatment and after that it began to give continuous excellent effective control (90-100% IE) for 5 successive weeks. These estimated times indicate that Dudim formulation proved to be more effective against C. pipiens larvae than formulations of Spinosad and VectoBac by about 1.4 and 2.2 times, respectively. Apart from lethal action, larval treatments with the test slow-release formulations led to a reduction in the mean number of eggs laid by mosquito female survivors during the 1st gonotrophic cycle but did not affect the hatchability of eggs.
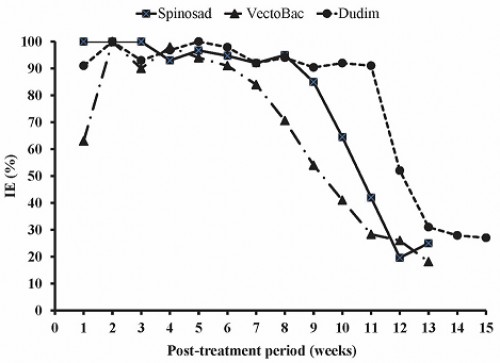 Fig.:
Fig.: Percentage emergence inhibition of
C. pipiens after treatment with sustain formulations of Spionsad, VectoBac and Dudim
How to cite this article:
Habeeb M Al-Solami. Larvicidal efficacy of three sustained insecticides against Culex pipiens larvae. Int J Mosq Res 2019;6(3):27-31.



