Investigation of Aedes aegypti’s resistance toward insecticides exposure using Markov modeling
Author(s): Atina Ahdika and Novyan Lusiyana
Abstract: Aedes aegypti is the vector of dengue infection. One of the methods to control the mosquitoes is the uses of temephos. However, continuous exposure of insecticides can cause resistance toward temephos. This research studied the Aedes aegypti’s behavior changes and its resistance toward continuous exposure of temephos. Three sample groups of Aedes aegypti from field (endemic and non-endemic) and from laboratory were collected. Larvae used in this research are 80 from field and 80 from laboratory. The samples are divided into eight groups and tested its resistance towards sublethal doses of temephos (0.00375 and 0.005 ppm) and modeled using Markov modeling. Mosquitoes group which has the most severe resistance is the group from endemic area of 4th instar which is given by 0.00375 ppm of temephos with the life time over 463.50 hours. While mosquitoes group which has the least resistance is the group from laboratory of 3rd instar which is given by 0.005 ppm with life time over 5.28 hours. Different origin, insecticide doses, and instar level can cause different effect on the mosquito’s resistance.
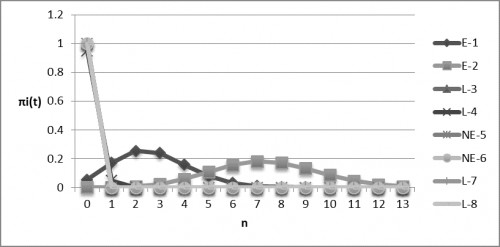 Fig.:
Fig.: Probability that there are Mosquitoes after 24 Hours
How to cite this article:
Atina Ahdika, Novyan Lusiyana. Investigation of Aedes aegypti’s resistance toward insecticides exposure using Markov modeling. Int J Mosq Res 2018;5(4):44-50.



