Larvicidal activity of castor oil Nanoemulsion against malaria vector Anopheles culicifacies
Author(s): Nisha Sogan, Neera Kapoor, Smriti Kala, PK Patanjali, BN Nagpal, Kumar Vikram and Neena Valecha
Abstract: Malaria is a vector borne disease, which is caused by Plasmodium parasite that is transmitted to humans through the bite of the Anopheles mosquito leading to transmission of the disease in countries of Southeast Asia including India. The problem of persistent toxicity along with the growing incidence of insect resistance, has led to the shift from synthetic to green pesticide. Castor oil (Ricinus communis) based nanoemulsion has been developed for large field breeding mosquitoes like Anopheles culicifacies. Castor oil nanoemulsion was formulated in different ratios comprising of castor oil, surfactants and water by High Pressure Homogenizer Mixer. The ratio of castor oil (10%) and surfactants (18%) was found to be stable. The castor oil nanoemulsion was characterized by dynamic light scattering and the PDI (polydispersity index )of the nanoemulsion was found to be 0.02. Castor oil nanoemulsion was screened for its efficacy against An. culicifacies using WHO protocol and compared with the bulk emulsion having droplet size of 118µm. The 24 h LC50 for castor oil nanoemulsion and castor bulk emulsion was found to be 3.4 and 52.31ppm, respectively. A botanical nanoformulation has been developed which is biodegradable, environment and user friendly.
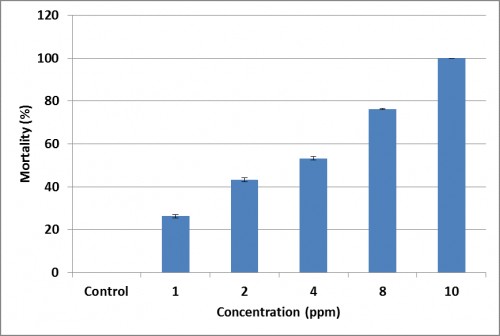 Fig.:
Fig.: Percent mortality of
An. culicifacies larvae within 24 hrs of treatment with castor oil nanoemulsion
How to cite this article:
Nisha Sogan, Neera Kapoor, Smriti Kala, PK Patanjali, BN Nagpal, Kumar Vikram, Neena Valecha. Larvicidal activity of castor oil Nanoemulsion against malaria vector Anopheles culicifacies. Int J Mosq Res 2018;5(3):01-06.



