Coupling of an agent-based model with a mathematical model of water pond dynamics for studying the impact of animal herd mobility on the Aedes vexans mosquito populations
Author(s): Python Ndekou Tandong Paul, Alassane Bah, Papa Ibrahima Ndiaye and Jacques André Dione
Abstract: In this paper, an agent-based model coupled with water pond dynamics was used to describe interactions between mosquitoes, hosts, water ponds in a virtual environment taking into account climatic factors. The objectives of the developed model were to build a virtual environment with the multi-agent platform CORMAS containing virtual mosquitoes and its behaviors, virtual hosts and its behaviors, virtual water ponds and its behaviors and used the data coming from interactions between virtual agents to study the impact of animal herd mobility in search of a water ponds on the growth of the mosquito populations. The results showed that, in the period of heavy rains, when the distance traveled by animal herd increase, the mosquito populations also increased. The different simulations showed that the growth of the number of mosquitoes in each water pond agent depends on the degree of animal herd mobility. The present study provides a framework that permits the control of the dynamics of mosquito populations in the virtual environment taking into account the mobility of animal herd and climatic factors.
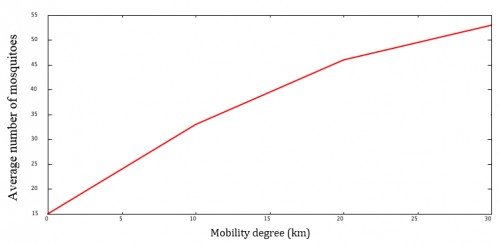 Fig.:
Fig.: Average number of mosquitoes as function of degree of mobility.
How to cite this article:
Python Ndekou Tandong Paul, Alassane Bah, Papa Ibrahima Ndiaye, Jacques André Dione. Coupling of an agent-based model with a mathematical model of water pond dynamics for studying the impact of animal herd mobility on the Aedes vexans mosquito populations. Int J Mosq Res 2017;4(3):132-141.



