Assessment of heavy metal concentration on Aedes mosquito breeding sites in urban area, Malaysia
Author(s): Nazri Che Dom, Pirdaus Ahmad, Megat Azman Megat Mokhtar and Shantakumari Rajan
Abstract: The aim of the present study is to establish a baseline of the existing level of heavy metals concentration in positive Aedes mosquito larval habitat in the selected dengue hotspot area and non-hotspot area. Aedes survey was conducted in Subang Jaya Municipality areas to assess the concentration and distribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Mn and Zn) in mosquito larval habitat. Water samples were (n = 141) collected and were analyzed using Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS) and other standard laboratory protocols. Then, by using microscope, Aedes larvae species was determined and the weight of pupae and length of 3rd instars larvae was measured. The concentration of heavy metal in dengue hotspot area was found to be relatively higher than corresponding level on the non-hotspot area at all breeding site investigated. Consistent with other finding, the present study proves that the heavy metal concentration varies between container material and its concentration. Overall, the key dengue vectors are preferential adapted with the heavy metal concentration and thus may affect the development and its lifecycle.
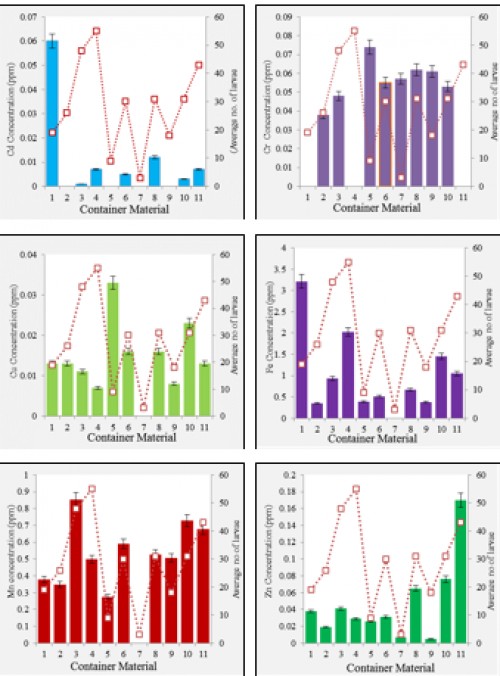 Fig.:
Fig.: Distribution of each heavy metal concentration by container material (1) Aluminium, (2) Concrete, (3) Ceramic, (4) Fiber, (5) Glass, (6) Metal, (7) Paper, (8) Plastic, (9) Polystyrene, (10) PVC, (11) Rubber.
How to cite this article:
Nazri Che Dom, Pirdaus Ahmad, Megat Azman Megat Mokhtar, Shantakumari Rajan. Assessment of heavy metal concentration on Aedes mosquito breeding sites in urban area, Malaysia. Int J Mosq Res 2017;4(2):12-19.



