Prevention and control of dengue by diet therapy
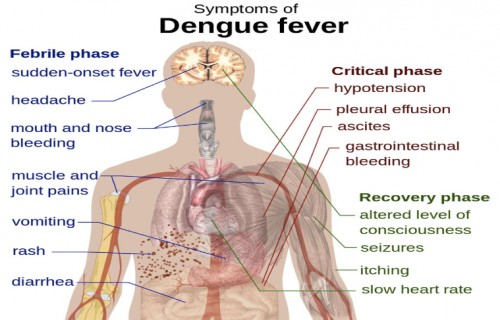 Fig. 1:
Fig. 1: .
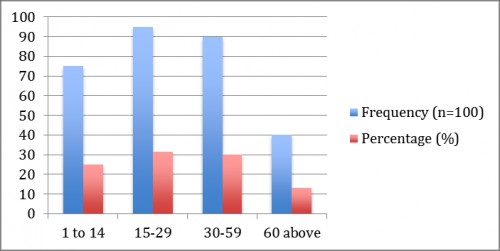 Fig. 2:
Fig. 2: shows that patients were belonging to different age groups 25% were 1 to 14 years, 31.6% were 15 to 29 years, 30% were 30 to 59 years and 13.3% were above the 60.
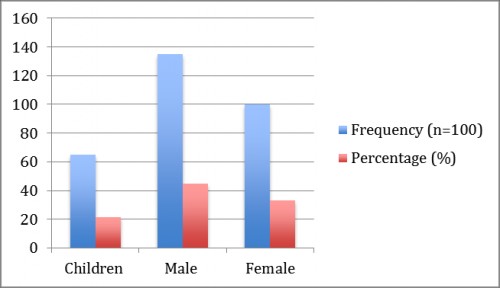 Fig. 3:
Fig. 3: shows that the dengue patients were selected for the study in which 21.6% are children’s, 45% were male and 33.3% were females.
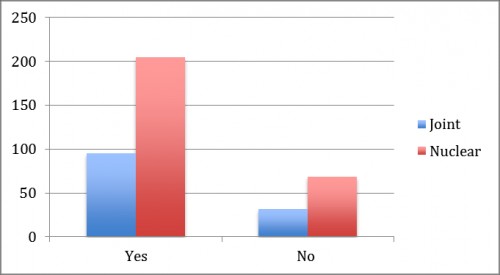 Fig. 4:
Fig. 4: shows that the dengue patient were 68.3% were belonging to nuclear family and 31.6% were belonging to joint family.
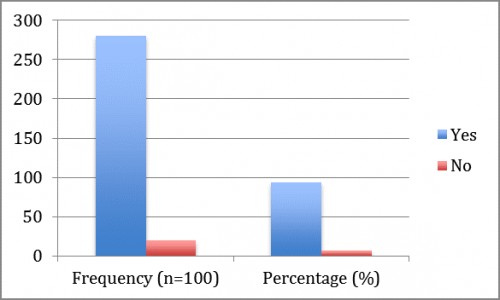 Fig. 5:
Fig. 5: shows that 93.3% patients were suffering from fever during dengue and 6.6% patients had not fever.
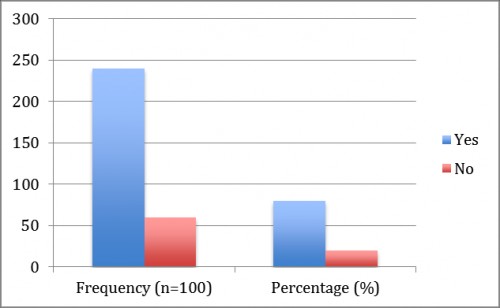 Fig. 6:
Fig. 6: shows that during dengue 80% patient were suffering from vomiting and nausea and 20% patients were not vomiting and nausea.
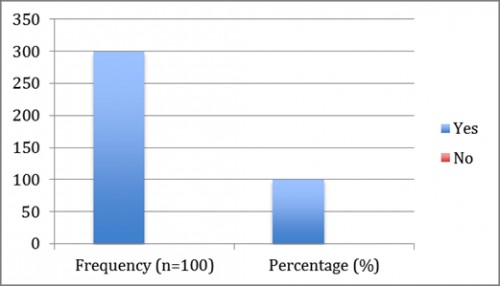 Fig. 7:
Fig. 7: shows that all the patients (100%) have electrolytes imbalance during dengue.
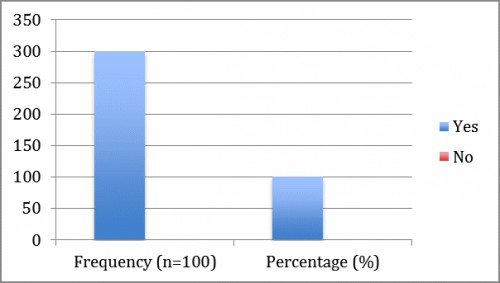 Fig. 8:
Fig. 8: shows that all the (100%) intervene with liquids.
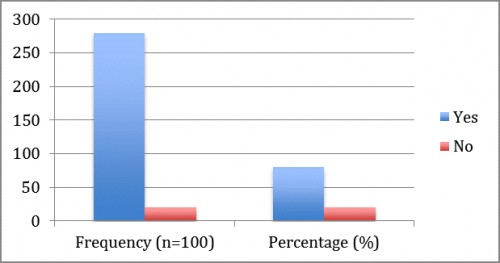 Fig. 9:
Fig. 9: shows that after taking the liquids 80% patients have balanced electrolytes and 20% were not
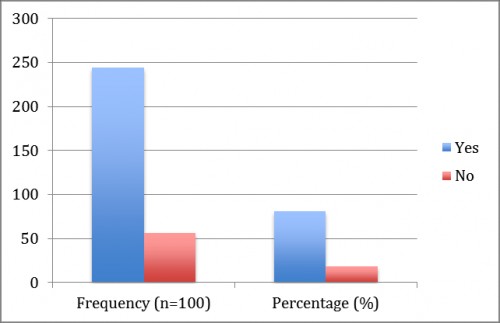 Fig. 10:
Fig. 10: Shows that the patients (81.3%) who were intervene with liquids and diet will be increase appetite and maintain the good nutritional status and 18.6% patients were not increased their appetite and nutritional status











