Biting rhythm of vector mosquitoes in a rural ecosystem of south India
Author(s): Paramasivan R, Philip Samuel P, Selvaraj Pandian R
Abstract: Mosquitoes transmit a variety of pathogens to man and understanding its biting periodicity helps to reduce the man-vector contact, which is a crucial factor for pathogen transmission. An in-depth field study was undertaken to determine the biting pattern and the biting rhythm of vector mosquitoes in the rural areas of Sivaganga district, Tamil Nadu, south India during 2006-2008. Three types of rhythmic biting patterns namely; nocturnal, diurnal and crepuscular were observed in the study area and a few species of mosquitoes found exhibited a restricted pattern of biting behavior. Moreover, it was found that a temporal variation in the biting pattern of mosquitoes and the adaptive feature of avoiding competition among themselves by sharing the available vertebrate hosts in the rural areas during the different periods in the diel cycle, which is very important for implementing vector control strategies to prevent man – vector contact for the prevention of vector borne diseases.
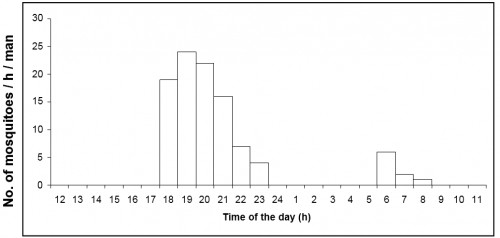 Fig.:
Fig.: Number of
Armigeres subalbatus caught per man hour
How to cite this article:
Paramasivan R, Philip Samuel P, Selvaraj Pandian R. Biting rhythm of vector mosquitoes in a rural ecosystem of south India. Int J Mosq Res 2015;2(3):106-113.



