Agnimantha: An herbal larvicide and pupicide against malarial vector Anopheles stephensi
Author(s): Shivaji Kashte, Subhash Walke, Navnath Parwe, Ramjan Mulani
Abstract: Malaria has 85% global infectious disease burden spread over 90 countries and territories in the tropical and subtropical regions. Worldwide next to Africa, in the South East Asia, India has the highest 77% malarial burden. Amid of various methods to control vector-borne diseases, vector control is a superior alternative. As larvicidal resistance is increasing among mosquitoes, herbal stratagems are forthcoming. In this study, antilarval and antipupal activities were carried out by using aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of Clerodendrum phlomidis against early fourth instar larvae and pupae of Anopheles stephensi. The result indicates that the aqueous and ethanolic leaf extract of Clerodendrum phlomidis have larvicidal and pupicidal activity as a green-collar approach for mosquito control.
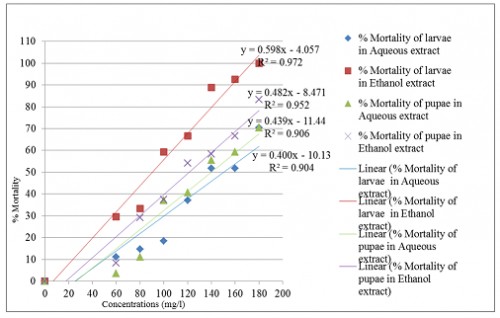 Fig.:
Fig.: % Mortality of larvae and pupae of Anopheles stephensi in aqueous and ethanolic extract of Clerodendrum phlomidis
How to cite this article:
Shivaji Kashte, Subhash Walke, Navnath Parwe, Ramjan Mulani. Agnimantha: An herbal larvicide and pupicide against malarial vector Anopheles stephensi. Int J Mosq Res 2015;2(3):89-93.



