Vol. 1, Issue 4, Part A (2014)
Status of insecticide resistance and detoxifying enzyme activity of Aedes albopictus population in Sonitpur district of Assam, India
Author(s): Momi Das and Prafulla Dutta
Abstract: Sonitpur district, Assam (India) is well known for malaria incidence since many years. The extensive use of insecticides for the control of malaria and other vector species is being carried out for vector management. The insecticide resistance status of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) to DDT (dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane) and deltamethrin was studied in the Sonitpur district of Assam. Even today DDT is the most widely used insecticides for public health programs in India. Recent information on the level of resistance to DDT and deltamethrin in an Aedes mosquito population of North East India is scarce. Continued monitoring of insecticide resistance status and identification of the underlying mechanism of resistance in the Aedes mosquito population is of prime importance. Insecticide susceptibility assays were performed on wild-caught adult female Aedes albopictus mosquitoes to the discriminating doses of DDT (4%) and deltamethrin (0. 05%) recommended by the World health organization (WHO). In all study sites, mortality as a result of DDT varied from 40.2 to 80.2% as compared to 94.2% in the susceptible laboratory strain (S-lab), indicating that Ae. albopictus is resistant to DDT in all study sites except Gohpur. The species was found to be 100% susceptible to deltamethrin in all study sites. Results from biochemical assays demonstrated increased alpha esterase, beta esterase and glutathione - S-transferase activity of Aedes albopictus at all study sites. Therefore, alpha esterase, beta esterase and glutathione - S-transferase activity seems to be associated with mechanisms responsible for insecticide resistance in Ae. albopictus. The results presented here provide the first report and baseline information about the insecticide resistance status of Ae. albopictus in North East India, and associated information about biochemical mechanisms that are essential for monitoring the development of insecticide resistance in the area.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics
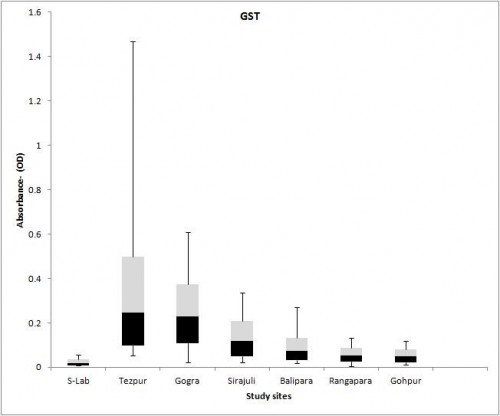
Fig.: Box plot distributions of absorbance values for (c) glutathione S- tranferase in field populations of Aedes albopictus
Pages: 35-41 | 2113 Views 268 Downloads
How to cite this article:
Momi Das, Prafulla Dutta. Status of insecticide resistance and detoxifying enzyme activity of Aedes albopictus population in Sonitpur district of Assam, India. Int J Mosq Res 2014;1(4):35-41.







