"International Journal of Mosquito Research"
Vol-1, Issue-3
Larvicidal activity of methanolic leaf extracts of plant, Chromolaena odorata L. (Asteraceae) against vector mosquitoes
Jagruti H. Sukhthankar, Hemanth Kumar, M. H. S. Godinho, Ashwani Kumar
Mosquitoes transmit malaria, filariasis, dengue, chikungunya, etc. Repeated use of insecticides for mosquito control has caused development of resistance, adverse effects on non-target organisms and serious environmental concerns. Hence alternative control measures are being explored inter alia plant based insecticides. We carried out larvicidal bioassays with methanolic extract of leaves of Chromolaena odorata (family Asteraceae) against late instar larvae of disease vectors Anopheles stephensi, Culex quinquefasciatus and Aedes aegypti. The highest mortality was observed in Cx. quinquefasciatus [LC50 = 43 ppm, (95% CI: 34 - 48 ppm); LC90 = 110 ppm (CI: 94 - 135 ppm)] followed by Ae. aegypti [LC50 = 138 ppm, (CI: 121 - 157 ppm); LC90 = 463 ppm (CI: 386 - 584 ppm)] and An. stephensi [LC50 = 1613 ppm (CI: 1364 - 1890 ppm); LC90 = 8306 ppm (CI: 6598 - 11076 ppm)]. Being larvicidal, leaf extracts of Chromolaena odorata could be explored further.
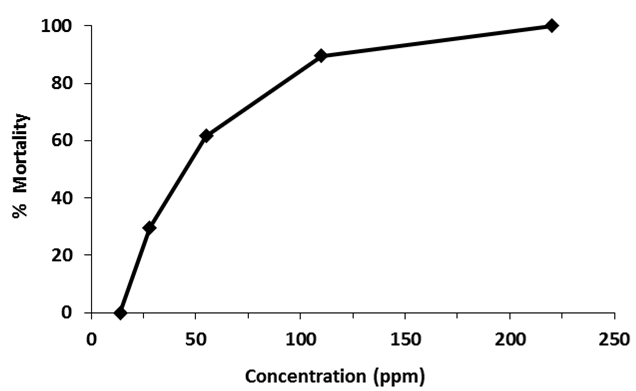
Fig: Bioassay of leaf extract of C. odorata against 3rd/4th instar larvae of Culex quinquefasciatus
Download Full Article: Click HereClick Heresee
