Vol. 4, Issue 1, Part A (2017)
Evaluation of wild tilapia and gift tilapia as biological control against mosquito larvae (Culex quinquefasciatus and Aedes aegypti)
Author(s): Shaheen Bibi, Mazhar Qayyum, Afzal Naseem, Dilawar Khan, Sakhawat Ali, Muhammad Sami-ur-rehman, Muhammad Rehan Aslam and Ajmal Khan Kassi
Abstract: In present study experiments were conducted on predation efficiency of Wild and GIFT tilapia on two different mosquito species 4th larval instar (Culex quinquefasciatus, Aedes aegypti) in laboratory controlled conditions to consider the number of parameters like fish size, temperature and feeding time at Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi. Tilapia fish is an efficient biocontrol agent against mosquito born diseases and have been used in controlling mosquitoes. Results showed that Wild tilapia prey consumption rate was greater at higher temperature 30o C (388±4.590) and less at low temperature 20o C (72.5±4.4319). Feeding of Wild tilapia showed maximum perdition efficiency in morning time (246.67±5.03) and minimum at afternoon and evening time (93.66±3.82 and 31.00±4.07 respectively). Considering the fish size in term of body weight predation rate increases with increasing body size. Wild tilapia is more efficient biocontrol agent against mosquito larvae (C. quinquefasciatus and A. aegypti) at 30o C temperature in morning time as compared to GIFT tilapia.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics
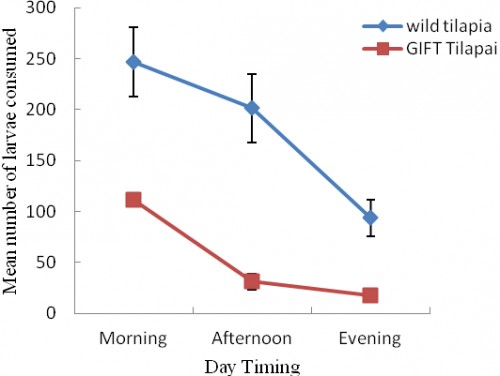
Fig.: Consumption rate of fish (Wild and GIFT) Tilapia at different timing of day.
Pages: 23-27 | 3246 Views 267 Downloads
How to cite this article:
Shaheen Bibi, Mazhar Qayyum, Afzal Naseem, Dilawar Khan, Sakhawat Ali, Muhammad Sami-ur-rehman, Muhammad Rehan Aslam, Ajmal Khan Kassi. Evaluation of wild tilapia and gift tilapia as biological control against mosquito larvae (Culex quinquefasciatus and Aedes aegypti). Int J Mosq Res 2017;4(1):23-27.







