Vol. 2, Issue 3, Part C (2015)
A longitudinal study on abundance and infection frequency of Japanese encephalitis vectors in Tirunelveli district, Tamil Nadu, India
Author(s): V Thenmozhi, T Balaji, A Selvam, K Venkatasubramani, KJ Dhananjeyan
Abstract: Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is transmitted by Culex vishnui subgroup, primarily Culex tritaeniorhynchus Giles, and amplified by infection of pigs / Ardeidae birds in nature. A longitudinal study of vector abundance and infection frequency of JE vectors was conducted from 2011-2013 in 4 villages namely Senthimangalam, Ariyanayagipuram, Kuthalaperi and Magiladi of Tirunelveli district. A total of 13, 343 adult mosquitoes were collected and processed by antigen capture ELISA. JEV was detected from ten species of mosquitoes – 28 positive pools, viz. Cx. tritaeniorhynchus (10), An. subpictus (7), Cx. infula (2), Ma. annulifera (2), Ma. uniformis. (2), Cx. bitaeniorhynchus (1), Cx. quinquefasciatus (1), An. pallidus (1) An. barbirostris (1) and Ar. subalbatus (1). Vector incrimination with JEV indicating a possible public health threat in the near future and helps programme people to develop appropriate control strategies.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics
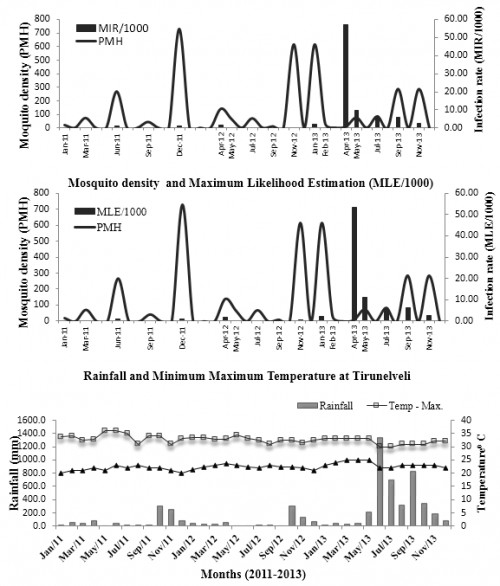
Fig.: .
Pages: 166-169 | 2126 Views 70 Downloads
How to cite this article:
V Thenmozhi, T Balaji, A Selvam, K Venkatasubramani, KJ Dhananjeyan. A longitudinal study on abundance and infection frequency of Japanese encephalitis vectors in Tirunelveli district, Tamil Nadu, India. Int J Mosq Res 2015;2(3):166-169.







